Middlewares
Concept
🔖
Goa middleware is a stand-alone plug-in that runs through the entire goa back-end application and shares context.
It should be clear that all functions of goa are implemented through middleware. If your application is not bound to any middleware, then your application is useless.
Graphical Middlewares
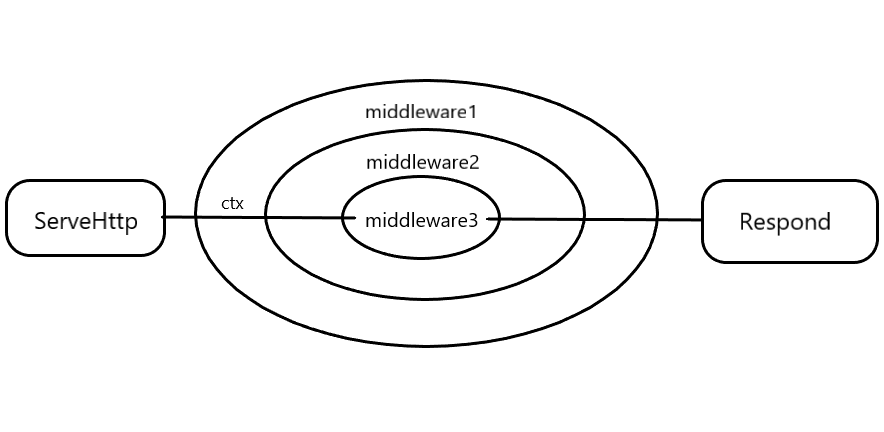
You can see that goa's middleware is executed in the form of a stack, and it is worth mentioning that goa's response handling is unified after all the middleware is executed.
app.Use(func(c *goa.Context) {
fmt.Pritln(1)
c.Next()
fmt.Println(6)
})
app.Use(func(c *goa.Context) {
fmt.Pritln(2)
c.Next()
fmt.Println(5)
})
app.Use(func(c *goa.Context) {
fmt.Pritln(3)
c.Next() // Not necessary in the last middleware.
fmt.Println(4)
})
The above programs output 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 in turn.
Example
r.GET("/", func(c *goa.Context) {
c.String("Hello World")
})
app.Use(logger.New())
app.Use(jwt.New(...))
app.Use(r.Routes())
Three middleware, logger, jwt and router, are used here.
Context will pass through logger - > jwt - > router - > jwt - > logger in turn.
Develop Middleware
We recommend the following practices for developing middleware:
type Config struct {
...
}
func New(Config) goa.Middleware {
// handle parameters or initialization
return func(c *Context) {
// ...
}
}
// use it
app.Use(XXX.New(...))
We recommend using this closure to improve performance. Of course, parameters are not necessary. The actual development should be combined with the actual situation, and this development mode isn't forced to use.
AWESOME
Official Middleware
← Context